Having a website is all about getting visibility and reaching your target audience. Search Engine Optimisation is an important tool for website owners to expand their organic reach and avoid spending too much on paid online marketing.
In today's post, we discuss sitemaps, a fundamental element of your website that helps search engines navigate and index your website.
We will explore the different types of sitemaps and their utility in Search Engine Optimisation and also touch upon certain dos and don'ts for creating the ideal sitemaps.
Table of Contents |

What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap file provides search engines with information about the pages, videos, documents, and other files on your website, and how these elements relate to each other. Search engine crawlers use this information to crawl websites in a systematic manner and regularly index the most significant parts of your website.
Having a sitemap is especially important if your website has a large number of pages, or isolated pages which are not well linked internally.
Types of Sitemaps
There are two main types of sitemaps, XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps. Each type serves a unique purpose and offers different SEO benefits for your website.
XML Sitemap
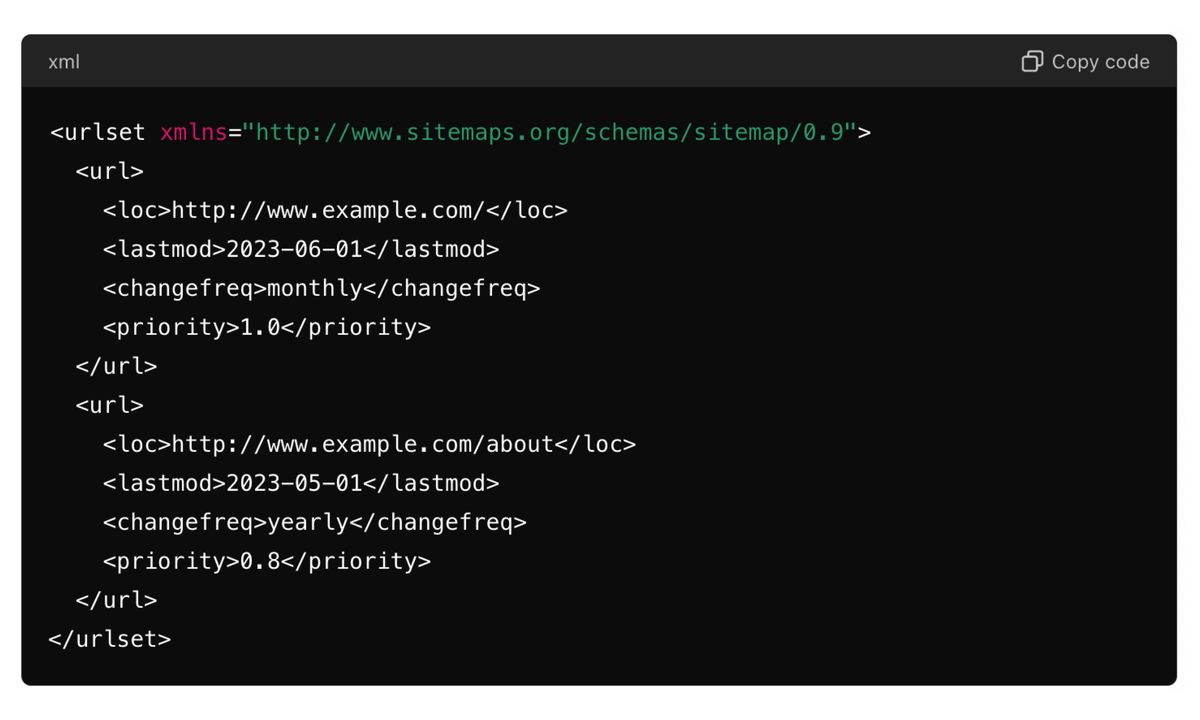
An XML sitemap is designed for search engine crawlers. It provides the search engine with a structured list of all pages on your website, to allow quick and effective indexing. Having an XML sitemap is highly recommended for new websites, websites with dynamic content, and for websites that have pages that are not easily discoverable through internal links.
Features of XML Sitemaps:
- Listing URLs to make it easier for search engines to find all your content.
- Including metadata such as publishing date, last modified date, frequency of updates, and page priority relative to the homepage on the site.
Sample Code for XML Sitemap:
HTML Sitemap
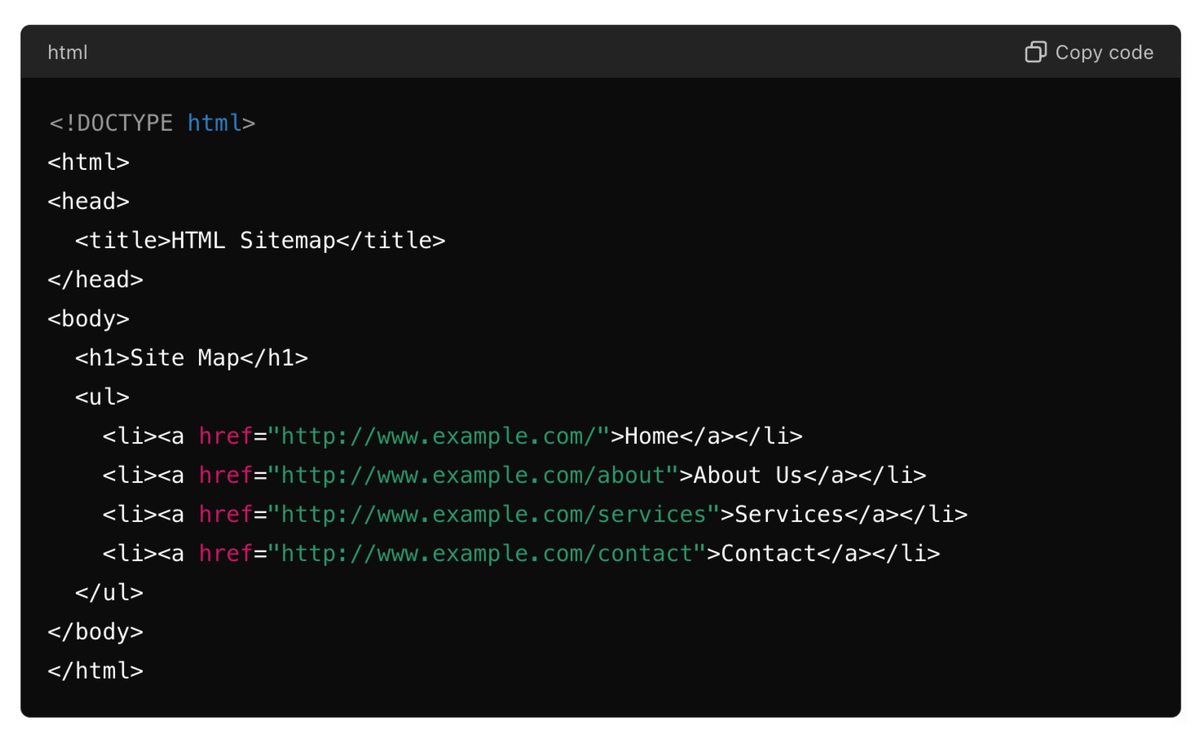
The HTML sitemap is a user-facing sitemap. It provides a user-friendly overview of the website structure and helps users quickly reach the content they seek.
While not directly impacting search optimization, HTML sitemaps do help in SEO by improving the User Experience (UX).
Features of HTML Sitemaps
- Acts as a navigational tool for the users
- Improves the User Experience, which is fast becoming a key SEO parameter that defines user stickiness and reduces bounce rates.
Sample Code for HTML Sitemap:
Importance of Sitemaps in SEO
Search engines like Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, etc. use sitemaps to find and index website pages. There are three elements that cover the entire process:
- Discovery: Search engine crawlers use sitemaps to identify all pages on your website, including pages which are dynamically generated and may not be well linked within the site structure. Thus, sitemaps ensure that all your content is discovered by the search engines.
- Crawling: Sitemaps also help search engines in crawling the website more effectively, according to the assigned priority of the pages. This ensures that the most important pages on your website are crawled and indexed to be shown in the search results.
- Indexing: It is the process of filing away the URLs by search engines to be displayed in search results. Sitemaps provide important parameters like the date of publication or the last modified date to indicate the freshness and relevance of the content, which can be a ranking factor as well.
Next up, let's learn how to create a sitemap.
Tools for creating XML Sitemaps
Generating a sitemap is usually easy and can be done with the help of tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or online platforms like www.xml-sitemaps.com. Website hosting platforms like WordPress, Wix, and Shopify also offer sitemap creation plugins that can be customized according to your requirements.
Moreover, if you have a custom website made using PHP, Python, or any other scripting language, creating a custom script to generate a sitemap can offer more control and customisation.
Best practices for creating XML Sitemaps
Here are some things to keep in mind when generating XML sitemaps:
1. Include Important Pages:
Focus on including pages that are valuable to both users and search engines. These typically include your homepage, major category pages, blog posts, and important product pages.
2. Keep it Updated:
Regularly update your sitemap to reflect new content, changes, or removed pages. Tools and plugins can help automate this process.
3. Avoid Duplicate Content:
Ensure your sitemap does not include duplicate content or pages with similar content. This can confuse search engines and dilute the value of your primary pages.
4. Use Metadata:
Include metadata in your XML sitemap to provide additional information about each URL. Metadata elements such as
5. Limit the Number of URLs:
Sitemaps are limited to 50,000 URLs or 50MB in size. If your site exceeds these limits, create multiple sitemaps and use a sitemap index file to reference them.
How to submit an XML sitemap?
Once your sitemap is created, the next step is to submit it to search engines. Here’s how to do it for the major search engines:
1. Google Search Console:
- Log in to Google Search Console: Go to the Search Console dashboard for your website.
- Navigate to the Sitemaps Section: On the left-hand sidebar, click on "Sitemaps."
- Submit Your Sitemap: Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml) in the "Add a new sitemap" field and click "Submit."
2. Bing Webmaster Tools:
- Log in to Bing Webmaster Tools: Access your website's dashboard.
- Navigate to the Sitemaps Section: On the sidebar, click on "Sitemaps."
- Submit Your Sitemap: Enter the URL of your sitemap and click "Submit."
3. Other Search Engines:
- For other search engines like Yahoo and DuckDuckGo, submitting your sitemap to Google and Bing is typically sufficient, as these engines often use similar indexing methods. However, you can also directly submit sitemaps via their webmaster tools if available.
Ensuring Successful Submission
After submitting your sitemap, it’s important to monitor its status to ensure it’s successfully processed:
1. Check Submission Status:
- Both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools provide detailed reports on your sitemap’s status. Check for errors or warnings and address any issues.
2. Monitor Indexing:
- Regularly review your indexing status in search console tools. Look for any pages that are not indexed and investigate potential issues.
3. Update and Resubmit as Needed:
- Whenever you make significant changes to your site structure or content, update your sitemap and resubmit it to the search engines.
What about HTML Sitemaps?
As mentioned earlier, HTML sitemaps are a part of your website's user experience. Since an HTML sitemap is a regular page on your website, typically linked at www.example.com/sitemap.html, it can be created and modified by the developer.
HTML sitemap does not require any submission to the search engines.
Also Read: The Crucial Role of Technical SEO
Concluding thoughts
Understanding the importance of sitemaps and integrating them into your SEO strategy can lead to better search engine rankings, increased organic traffic, and a more user-friendly website. Take action today by creating or updating your sitemap, and watch how this simple yet powerful tool can make a significant impact on your SEO success.
If you are looking for expert guidance on SEO and digital marketing, speak to an expert at DO Communication now.


